Results
Feature Importance
Looking more deeply at the random forest model that fit our data the best, we explored which features are actually important in predicting heating loads. In the graph below, the y-axis shows various features which were included in the model, and the x-axis shows their relative importance on a logarithmic scale. Feature importance can be described as a score assigned to features based on how significant they are at predicting a target variable.
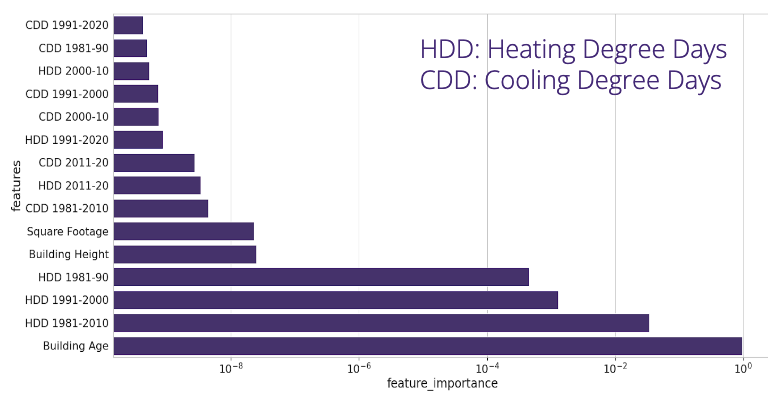 Age stands out as the strongest predictor. This can be expected, since older buildings might be less energy efficient and more prone to air leakage. However, this may also be due to the output used for model training, as it was interpolated from regressions of heating loads on age.
Age stands out as the strongest predictor. This can be expected, since older buildings might be less energy efficient and more prone to air leakage. However, this may also be due to the output used for model training, as it was interpolated from regressions of heating loads on age.
We also see that heating degree days averaged over 1981-2010 and 1991-2000 are relevant in predicting heating needs. This highlights that it may be important to take both recent and older climate data into account while estimating heating loads.
While these results are a part of a proof-of-concept exercise, they do have the potential to inform decarbonization policies like energy retrofitting in Alaska. For instance, the importance of the age variable as a predictor may answer if it is better to replace old buildings rather than retrofitting them to save energy.
Data Sampling
Data sampling is balancing data across selected factors to avoid biasing estimates. For example, our project identifies 108,776 buildings on the Alaskan Railbelt, with 31% (n= 33,990) of them outside Anchorage or Fairbanks— therefore lacking heating load estimates. However, among the buildings with heating load estimates, the large majority are in Anchorage. Therefore we explored whether balancing our data on location (i.e. Fairbanks vs. Anchorage) made a difference in the mean squared error of our models. We additionally balanced on our most salient feature: building age.
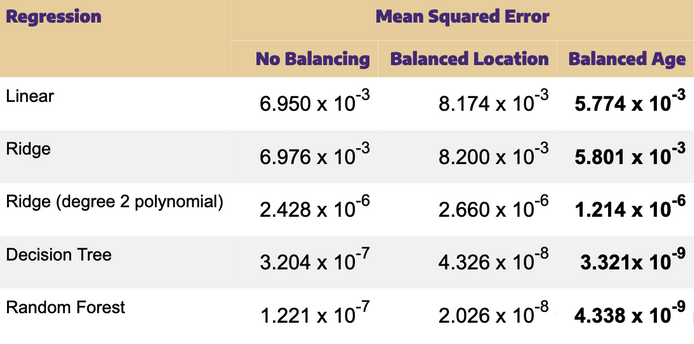
Balancing location made a difference with the decision tree and random forest models relative to the unbalanced models. By contrast, balancing age improved upon the unbalanced models for every model type.
Takeaways
- We produce the first Alaskan heating load estimates that capture variation in local climate
- These models allow prediction of future heating needs according to climate projections
- This work can immediately inform renewable energy and climate mitigation policies in Alaska