Topic modeling
NMF for recall vs. non-recall
It is assumed that all the code from the Data processing section of this website has been run before running any of the code below.
As a first pass, we evaluated the topics resulting for recalled products versus non-recalled reviews separately.
##Count Vectorizer Matrix
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfTransformer
import scipy
from scipy.sparse import csr_matrix, vstack
vectorizer = CountVectorizer(binary=False, ngram_range=(1, 1))
text_vector = vectorizer.fit_transform(final_text)
##Remove if word is in less than 2 reviews (uncomment if want to apply to the text corpus)
#counts = scipy.sparse.csr_matrix.sum(text_vector, axis=0)
#text_vector = np.transpose(vstack([text_vector,counts]))
#text_vector = pd.DataFrame(text_vector.todense(), index = vectorizer.get_feature_names())
#last_col = text_vector.shape[1] - 1
#text_vector = text_vector[text_vector[last_col] > 1]
#del text_vector[last_col]
#text_vector = text_vector.transpose()
##Make word count matrix with recall info and apply TF-IDF weighting
transformer = TfidfTransformer()
text_vector = transformer.fit_transform(text_vector)
text_vector = pd.concat([pd.DataFrame(text_vector.todense()), (pd.DataFrame(Subset.recalled_1y)).reset_index(drop=True)], axis=1)
##Separate into Recall vs. non-recall
text_vector_recall_1 = text_vector[(text_vector.recalled_1y == 1)]
text_vector_recall_1 = text_vector_recall_1.drop('recalled_1y', axis=1)
text_vector_recall = text_vector_recall_1.transpose()
text_vector_recall_sparse = scipy.sparse.csr_matrix(text_vector_recall)
text_vector_nonrecall_1 = text_vector[(text_vector.recalled_1y == 0)]
text_vector_nonrecall_1 = text_vector_nonrecall_1.drop('recalled_1y', axis=1)
text_vector_nonrecall = text_vector_nonrecall_1.transpose()
text_vector_nonrecall_sparse = scipy.sparse.csr_matrix(text_vector_nonrecall)
## Non-negative matrix factorization
import nimfa
nmf_nonrecall = nimfa.Nmf(text_vector_nonrecall_sparse, rank=50, seed='random_c', update="divergence", objective="div")
fit_nonrecall = nmf_nonrecall()
nsnmf_recall = nimfa.Nsnmf(text_vector_recall_sparse, rank=50, seed='random_c', update='divergence', objective='div')
fit_recall = nsnmf_recall()
##Terms and Weights Recalled Review
import seaborn as sns
sns.set(style="darkgrid", color_codes=True, font_scale=1.25, palette='bright')
feature_names = vectorizer.get_feature_names()
import matplotlib.pylab as plb
%matplotlib inline
def plot(W,termlist):
for c in range(W.shape[1]):
top10 = np.argsort(np.asarray(W[:,c].todense()).flatten())[-10:]
val = W[top10, c].todense()
plb.figure(c + 1)
plb.barh(np.arange(10) + .5, val, color=['LightSteelBlue', 'LightBlue', 'LightSkyBlue', 'DeepSkyBlue', 'DodgerBlue',
'CornflowerBlue','SteelBlue','RoyalBlue','MediumBlue', 'MidnightBlue'], align='center')
plb.yticks(np.arange(10) + .5, [feature_names[i] for i in top10][::-1])
plb.xlabel("Weight")
plb.ylabel("Term")
plb.title("Highest Weighted Terms in Basis Vector W%d" % (c + 1))
plb.grid(True)
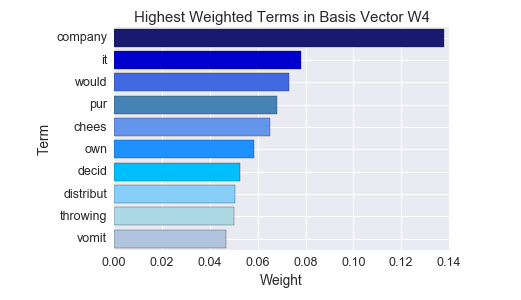
plot(fit_recall.basis(), feature_names)

It appears that some recall specific-topics emerge from the recalled products (an example is shown above - code prints 50 topics total when it is actually run). There are still many product-related topics, however.
##Terms and Weights NonRecalled
plot(fit_nonrecall.basis(), feature_names)
NMF with only 2 Star review or below
The code below runs topic modeling on only product reviews with 2-stars or lower. The idea behind this process was to see if unsupervised dimensionality reduction could pull out recall-topics among products that were all ‘bad’ from the consumers point of view. There was some success with this process (see example topic below)!
##Make word count matrix with rating
text_vector2 = text_vector.drop('recalled_1y', axis=1)
score_df = pd.DataFrame(Subset.overall).reset_index(drop=True)
score_df.columns = ['Score']
text_vector2 = pd.concat([text_vector2, score_df], axis=1)
text_vector2 = text_vector2[text_vector2.Score < 3]
##Transpose and Make sparse
text_vector2 = text_vector2.drop('Score', axis=1)
text_vector2 = text_vector2.transpose()
text_vector_sparse2 = scipy.sparse.csr_matrix(text_vector2)
## Non-negative matrix factorization
nmf = nimfa.Nmf(text_vector_sparse2, rank=50, seed='random_c', update="divergence", objective="div")
fit = nmf()
##Terms and Weights
plot(fit.basis(), feature_names)
NMF without product category words
The code below brings in the text from all categories in the Amazon review dataset, and removes these words from the review text. NMF is run on the resulting corpus, in order to see if removing category text helps to ‘control’ for product-specific topics. This approach had limited success, and a next step would be to apply NMF to each category type, and see if recall-specific topics emerge.
##Call in data that includes ASINs from original press release data
recall_data = pandas.read_csv(os.path.join(wd,"..","..","data/processed/asin_intersection_full.csv"),
encoding='ISO-8859-1')
## Define category words to be removed
category_terms = recall_data.categories.str.replace('[^a-zA-Z\s]',' ')
category_terms = category_terms.str.cat()
category_terms = word_tokenize(category_terms)
stemmed_category_terms = []
for word in category_terms:
stem = st.stem(word)
stemmed_category_terms.append(stem)
vectorizer_noncategory = CountVectorizer(binary=False, ngram_range=(1, 1), stop_words = stemmed_category_terms) ##Removed stopwords before stemming so don't apply here
text_vector_noncategory = vectorizer_noncategory.fit_transform(final_text)
text_vector_noncategory = transformer.fit_transform(text_vector_noncategory)
text_vector_noncategory_sparse = scipy.sparse.csr_matrix(text_vector_noncategory)
## Non-negative matrix factorization
nmf = nimfa.Nmf(text_vector_noncategory_sparse, rank=50, seed='random_c', update="divergence", objective="div")
fit_noncategory = nmf()
feature_names = vectorizer_noncategory.get_feature_names()
plot(fit_noncategory.basis(), feature_names)